LGBTQ Guide for Addiction Treatment
Table of contents
- What Are Substance Use Disorders?
- What Does LGBTQ+ Mean?
- LGBTQ+ Community Experiences Mental Health Issues at Higher Rates
- What Are the SUD Rates for the LGBTQ+ Community?
- Most Common Co-Occurring Disorders in LGBTQ+ Populations
- How do You Treat These Co-Occurring Disorders During Addiction Treatment?
- What Substances Are Most Abused in the LGBTQ+ Community?
- Challenges the LGBTQ+ Community Faces
- Trauma-Informed Care Approach in Addiction Treatment
- Addiction Treatment Options
- Resources
What Are Substance Use Disorders?
This article will provide an LGBTQ guide for addiction to help you learn how addiction affects the LGBTQ community as well as treatment options that are available. Substance use disorders, or SUDs, are characterized by the continual use of an addictive substance for a long time despite it having negative consequences on their life and well-being. When someone struggles with SUD, it can affect their life in many ways.
Due to many factors, such as discrimination and traumatic experiences, people in the LGBTQ+ community may be more susceptible to developing a substance use disorder. LGBTQ addiction is serious and it can yield many negative effects. Fortunately, addiction treatment for members of the LGBTQ+ community is available, and it can help people from all backgrounds get the help they need to recover.
The recovery process can be intense, but it does not have to done alone. Read on to learn more about the effects of addiction in the LGBTQ+ community and the best type of treatment options.
Questions about addiction?
Call Us Now: 1-866-232-9103
Your call is confidential with no obligation required to speak with us.
What Does LGBTQ+ Mean?
An Overview of LGBTQ+
Lesbian
Gay
Bisexual
Pansexual
Transgender
Non-Binary
Gender Non-Conforming
Questioning
Plus
Asexual
Gender Fluid
LGBTQ+ Community Experiences Mental Health Issues at Higher Rates
Due to many factors, people in the LGBTQ+ community statistically experience mental health issues, including depression, anxiety, and PTSD, at higher rates than other groups of people.
What are the Rates?
Why Might They Be So High?
Many people who identify with as LGBTQ+ may experience discrimination, have trouble expressing themselves, or placed in situations that heighten the likelihood of them experiencing trauma, all of which can lead to mental health issues and other negative effects on their lives.
Discussing the Challenges Faced by the LGBTQ+ Community
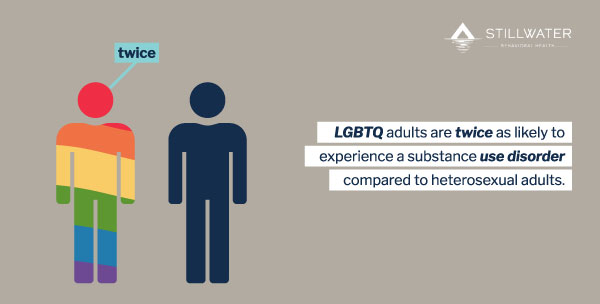
What Are the SUD Rates for the LGBTQ+ Community?
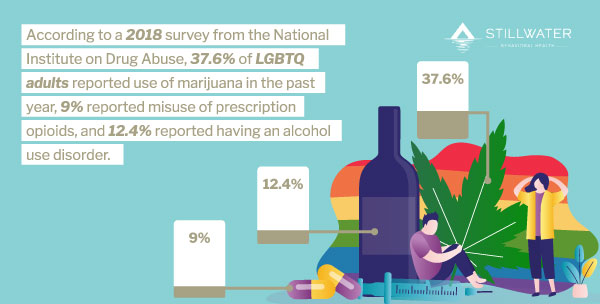
Due to the issues and difficulties that many people in the LGBTQ+ community face, LGBTQ addiction rates are also very high. According to a 2018 survey from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, 37.6% of LGBTQ adults reported use of marijuana in the past year, 9% reported misuse of prescription opioids, and 12.4% reported having an alcohol use disorder.3

How Do They Compare to Other Groups?
What Factors Underly the Substance Use Disorder Rates?
There are many factors that form the foundation of high LGBTQ addiction rates. Factors such as increased rates of rejection, trauma, and subsequent mental health issues all contribute to members of the LGBTQ community turning towards drugs and alcohol to cope.
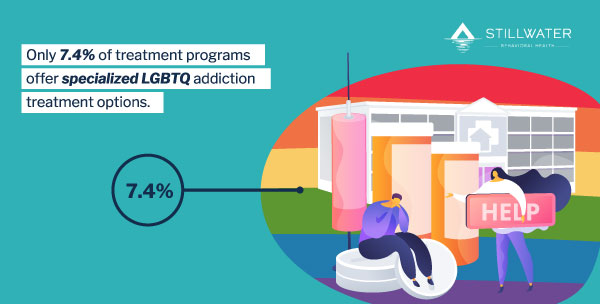
People in the LGBTQ community also tend to lack access to proper LGBTQ addiction treatment programs. The National Institute on Drug Abuse states that only 7.4% of treatment programs currently provide access to specialized LGBTQ addiction treatment, even though specialized options have shown much higher success rates in the treatment of LGBTQ drug addiction.
Most Common Co-Occurring Disorders in LGBTQ+ Populations
Bipolar Disorder in the LGBTQ+ Community
While there has not been extensive research conducted regarding the bipolar rates amongst members of the LGBTQ+ community, some studies have concluded that LGBTQ individuals may be more susceptible to the development of bipolar disorder, along with other mental health issues. Things such as rejection, trauma, and discrimination all contribute to mental health issues that can affect people in the LGBTQ community in various ways.
PTSD in the LGBTQ+ Community
Depression in the LGBTQ+ Community
Anxiety in the LGBTQ+ Community
Stress in the LGBTQ+ Community
A 2018 Human Rights Campaign survey showed that individuals from the LGBTQ community experience much higher stress levels compared to heterosexual individuals. 95% of LGBTQ respondents reported having trouble sleeping at night, 77% reported feeling depressed, and 26% reported that they didn’t feel safe at school.4
Suicide and Self-Harm in the LGBTQ+ Community
Gender Dysphoria and Addiction
Eating Disorders in the LGBTQ+ Community
Research has shown that approximately half of all LGBTQ individuals may struggle with an eating disorder at some point in their life.6 Many people in the LGBTQ community experience discrimination regarding their personal image, which often contributes to the development of an eating disorder.
Psychosis in the LGBTQ+ Community
Members of the LGBTQ community are also more likely to experience psychosis or severe mental illnesses compared to heterosexual people. This is often due to discrimination, high rates of trauma, and a lack of mental health treatment resources specifically designed for LGBTQ individuals.
How do You Treat These Co-Occurring Disorders During Addiction Treatment?
How Do Psychiatrists and Other Specialists Help Treatment of Co-Occurring Disorders?
Psychiatrists and other specialists can help with co-occurring disorders in many ways during LGBTQ addiction treatment. Psychiatrists are trained to properly diagnose and treat underlying conditions that an individual may have. Continued therapy and other resources can be used throughout treatment in order to get the best results in treating both the addiction and co-occurring conditions. It is imperative that both disorders are treating alongside one another because the two issues could feed into one another.
A Further Discussion on Addiction and the LGBTQ+ Community
What Substances Are Most Abused in the LGBTQ+ Community?
Alcohol
LGBTQ members can be more susceptible to alcohol addiction. When someone undergoes high amounts of stress, it can be easy to lean on alcohol and get into the habit of binge drinking. Alcohol is a substance that is commonly used to cope with mental health issues or traumatic experiences that may be causing someone distress.
Stimulants
Stimulant drugs may also be abused by LGBTQ members. Mental health issues, like post-traumatic stress disorder and anxiety, can cause insomnia, which might make someone want to lean on stimulant drugs for energy. Stimulants can be very addictive as they have the potential to cause a myriad of negative effects and undesirable impacts on someone’s life.
Opioids
Opioid addiction is also more common amongst the LGBTQ community. Opioid addiction affects many people every year, especially those who try to use opioids as a recreational substance or to self-medicate when dealing with various other underlying conditions.
Benzodiazepines
Challenges the LGBTQ+ Community Faces

Discrimination
Many LGBTQ members face a lot of discrimination in their daily lives. Many who come out to their families face rejection and negative feedback from family members. Other LGBTQ members also face discrimination every day at work, school, or even in their social lives.
Stigma
Abuse
Rejection
Unemployment
Homelessness
Trauma-Informed Care Approach in Addiction Treatment
Trauma informed care should be put in place during LGBTQ addiction treatment since LGBTQ individuals are much more likely to experience trauma at some point during their lives. This helps ensure the comfort and security of patients during the treatment process by understanding their trauma and how it affects them.
Realize
Recognize
Care that is trauma-informed also helps patients and care providers recognize the effects of trauma so they can work through underlying issues and begin to learn how to cope with the effects that trauma have had.
Responds
Avoid Re-traumatization
Addiction Treatment Options
Detox
Detox is one of the first steps in the treatment process. When someone first stops taking an addictive substance, they will experience withdrawal symptoms. Treatment centers can help patients get through this difficult period of the recovery process and make it as safe and as comfortable as possible.
Inpatient
Inpatient treatment involves staying at a treatment center for a duration of time while detoxing, receiving therapy, and working on a long-term plan for success. Inpatient treatment is a good option by putting patients in a stable environment that is away from temptations.
Outpatient
For those who struggle with an addiction that is less severe, outpatient treatment may be a good option. Outpatient rehab will allow you to continue living at home, so you don’t have to neglect family or work responsibilities while receiving treatment. Outpatient treatment requires that you go to a treatment center at designated times throughout the week to work on a treatment plan and receive therapy.
Medication-Assisted Treatment
Medication assisted treatment may also be used during the treatment program to help ease withdrawal symptoms and prevent a relapse from occurring. Many medications have been studied, tested, and developed to make the treatment process easier and more effective.
Resources
- https://www.verywellmind.com/what-does-lgbtq-mean-5069804
- https://www.nami.org/Your-Journey/Identity-and-Cultural-Dimensions/LGBTQI
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/lgbt-youth-and-mental-health#anxiety
- https://assets2.hrc.org/files/assets/resources/2018-YouthReport-NoVid.pdf
- https://www.thetrevorproject.org/research-briefs/estimate-of-how-often-lgbtq-youth-attempt-suicide-in-the-u-s/
- https://www.nationaleatingdisorders.org/learn/general-information/lgbtq


